Our outlook for the U.S. economy remains generally more optimistic than consensus, as we forecast stronger gross domestic product growth and lower inflation. We place the probability of recession risk at just 25% for the next two years.
With inflation already easing substantially without a recession, we’re very confident that the U.S. economy is capable of a soft landing, but achieving it is contingent on avoiding monetary policy error. Near-term growth in economic activity is proving more resilient to monetary policy tightening than we had anticipated, which is inducing the Federal Reserve to continue hike rates.
Still, we think the binary question of whether a recession will or won’t occur misses the point. Any recession is likely to be short-lived, and we expect GDP growth to rebound strongly in 2024.
Since our last update, we’ve hiked our GDP forecast, owing to stronger-than-expected near-term data, including the strong January jobs and retail sales reports.
We project a GDP growth rate of 1.4% for 2023, 1.7% for 2024, and much higher rates for 2025 through 2027. Overall, we expect a cumulative 3% to 4% more real GDP growth through 2027 than consensus does.
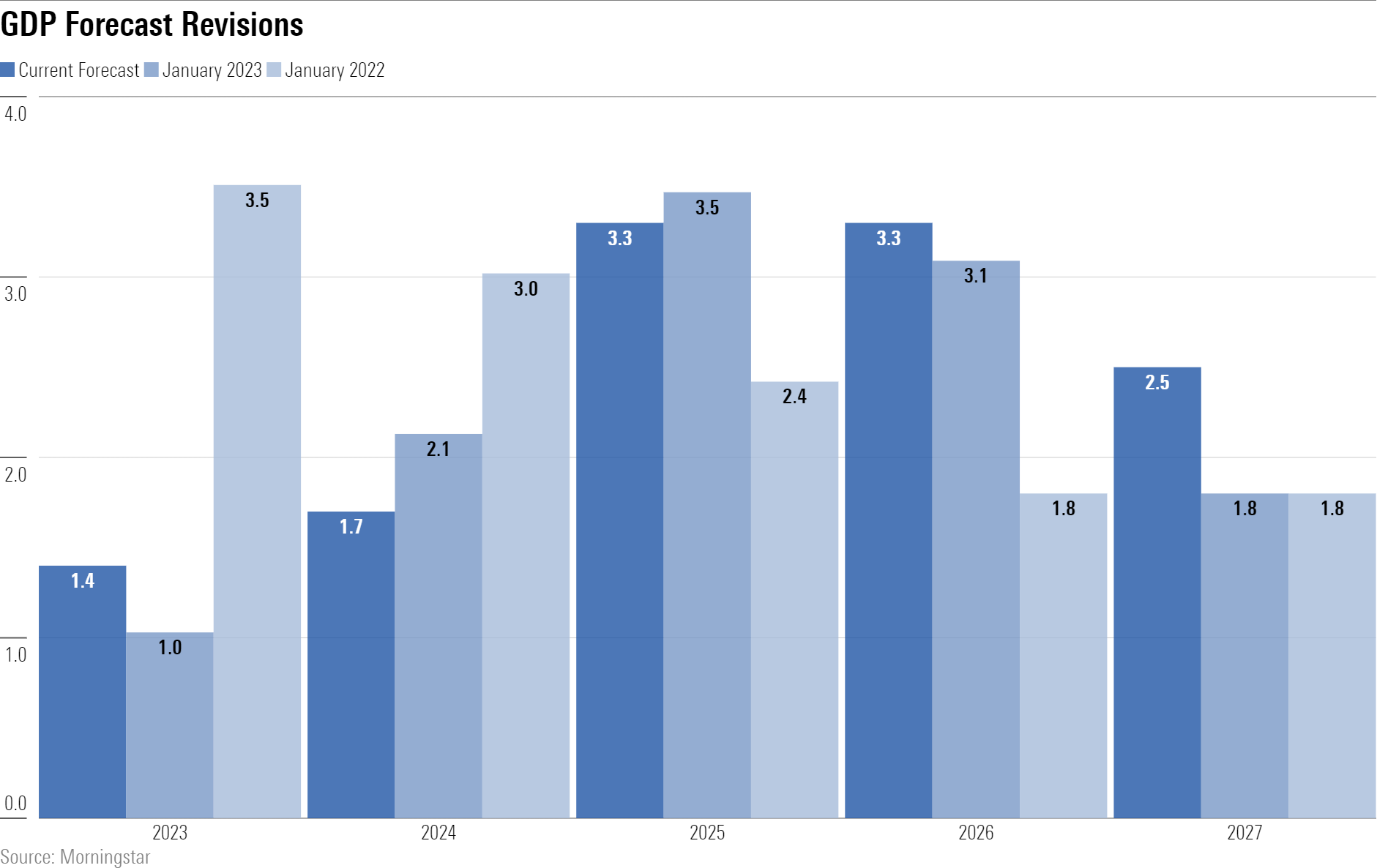
The chart shows that we expect a rebound in GDP growth in 2024 and the following years, triggered by a Fed pivot to monetary policy easing. This strong pace of GDP growth will be enabled by supply side expansion, including labour force expansion as well as solid productivity gains.
We Expect the Fed to Shift Back to Easing After Victory Over Inflation Looks Clear
Interest rates have soared over the past year as expectations of monetary policy tightening have built up and begun to play out.
Since our last update, we’ve hiked our near-term forecast—we expect a federal-funds rate of 4.92% and a 10-year Treasury yield of 3.75% for 2023 (full-year average). However, we still think rates will soon reach their top and expect the Fed to start cutting interest rates aggressively starting around the end of 2023 as inflation normalizes and the need to shore up GDP growth becomes paramount.
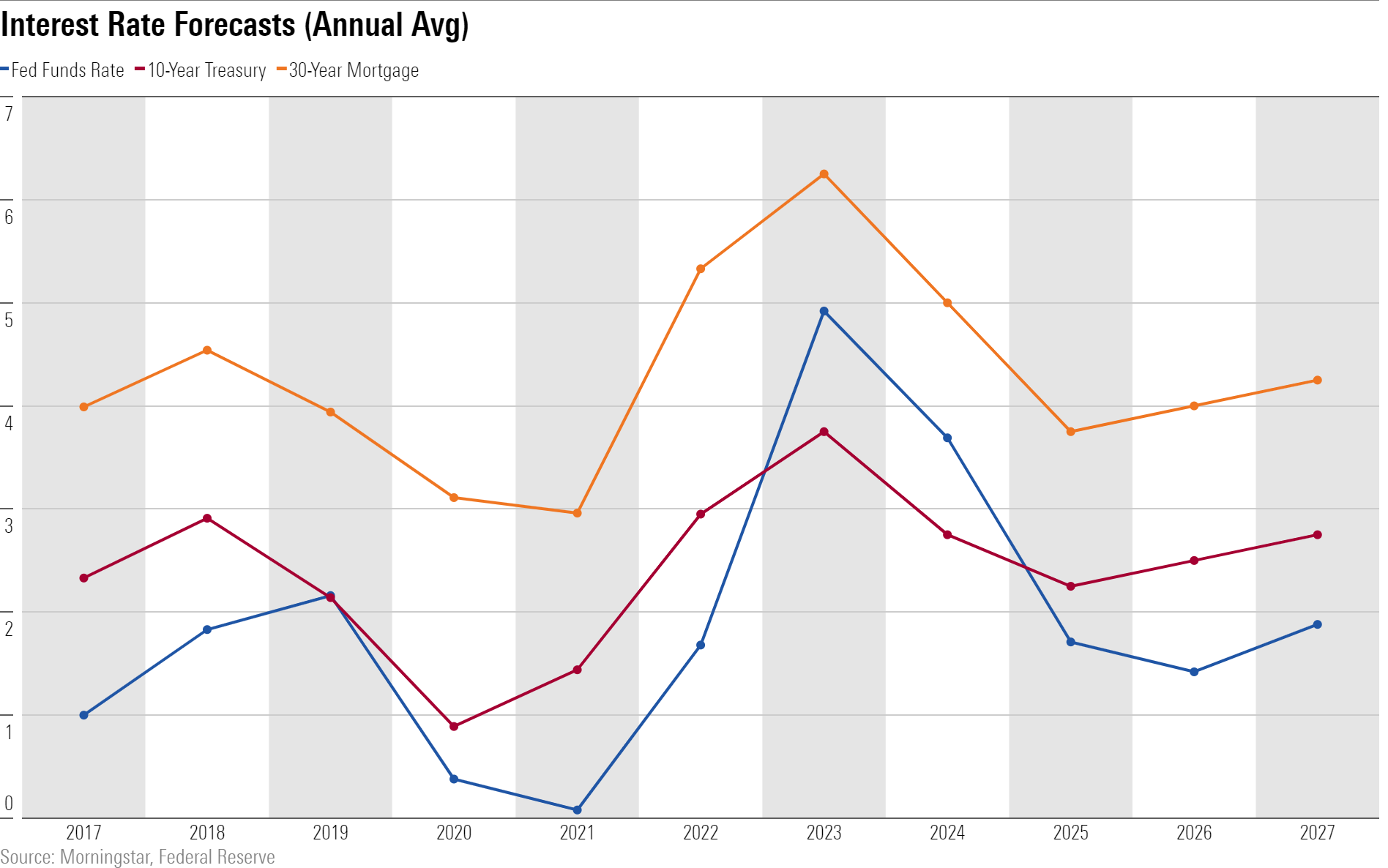
Bond markets still imply a too-restrictive path for monetary policy, with the five-year Treasury yield around 130 basis points higher than appropriate, given our expected path for the federal-funds rate. Lower interest rates will be needed to avert an even more severe downturn in the housing markets than is already likely to occur.
For now, the economy is weathering the impact of interest-rate hikes better than we anticipated, but we still expect that many lagged effects of rate hikes will weigh on the economy in 2023.
Inflation Should Return to Normal in 2023
A hotter-than-expected economy means that we’ve upped our inflation forecast slightly for 2023 on average, though we still expect inflation to end the year about in line with the Fed’s 2% target. A combination of easing supply constraints along with Fed tightening is winning the battle against inflation.
After peaking at 6.2% in 2022, we expect an inflation rate of 3.2% in 2023 before it falls substantially for an average of 1.9% over 2023-27.

This puts us at a more optimistic view than consensus, as we think most of the sources of inflation will unwind and aggressive capacity expansion will continue.
We think that many industries that experienced a large spike in prices since the start of the pandemic will experience deflation over the next several years. This includes energy, autos, and other durable goods. Aggressive capacity expansion across many areas could turn widespread shortages into gluts within a few years.
Falling goods price inflation have helped push the core inflation rate to 4.6% annualized in the past three months, down from 8.0% at the start of 2022. There’s still a long way to go in bringing inflation back to normal, but the fact that inflation has already fallen so far without a recession occurring is very encouraging.
GDP Growth Is Weaker Than Normal, but a Recession Hasn’t Occurred Yet
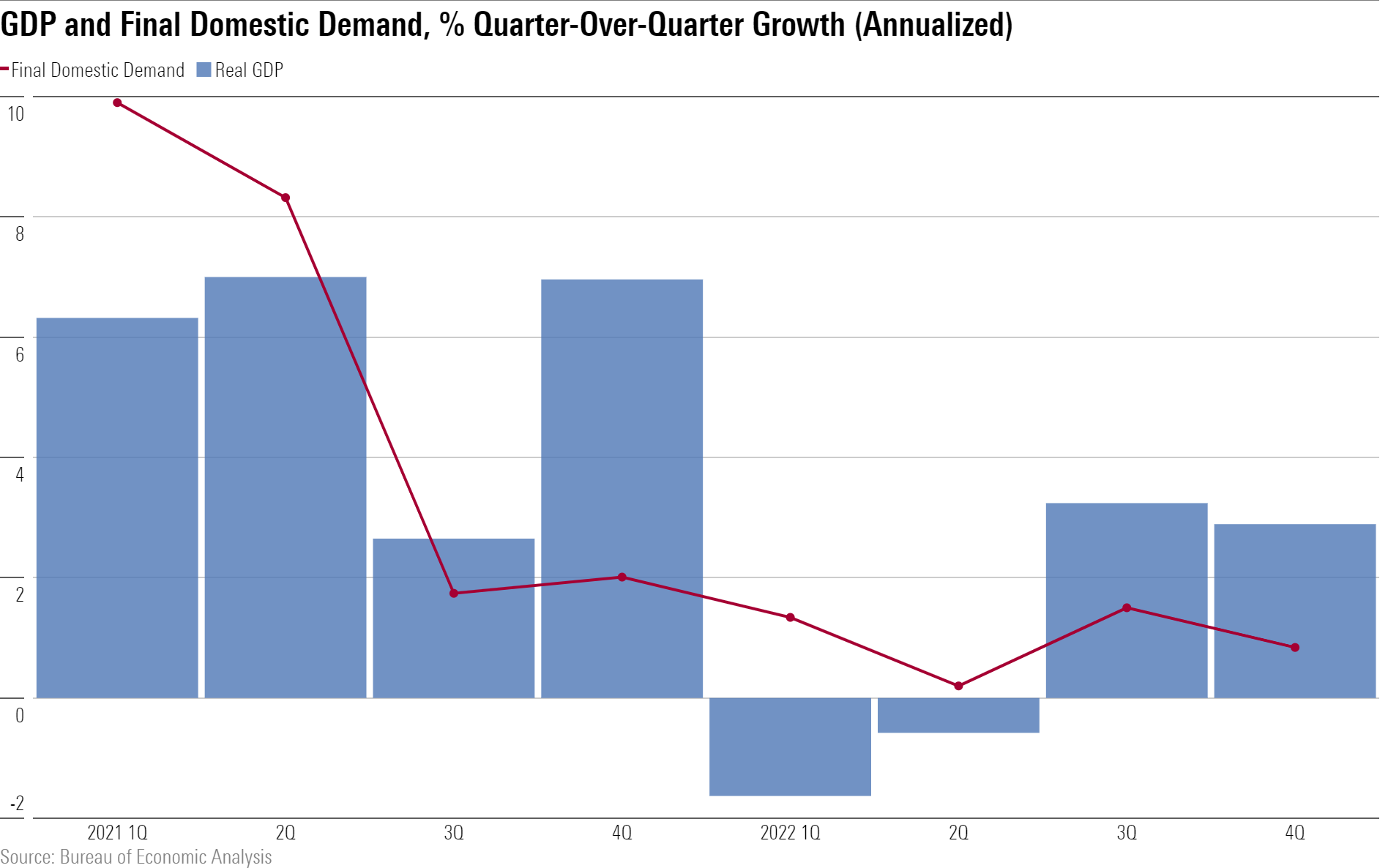
Though some observers claimed a recession in the first half of 2022, we’ve refuted this as we’ve seen the underlying trend in GDP growth remain consistently positive.
Much of the volatility in quarter-over-quarter growth numbers has been driven by inventories and net exports, which are consistently noisy components of GDP growth. Stripping out those components from GDP yields “final domestic demand” (consumption plus fixed investment), which is likely a better gauge of the underlying trend in GDP growth. Even in quarter-over-quarter terms, final domestic demand has been fairly stable since late 2021, with growth hovering between 1% and 2% annualized. Overall, the data points to an underlying trend in GDP growth that is below the 2.0% to 2.5% averaged in the prepandemic years but still positive.
What Could Happen to the U.S. Economy in 2023?
We map out four potential near-term scenarios for the U.S. economy:
- Soft landing: This is our base case, meaning that we see inflation returning to normal by the end of 2023, even as real GDP growth remains positive in year-over-year terms.
- Stagflation: This scenario sees a far more unfavorable inflation/growth trade-off. Those in the stagflation camp point to a labour market still at record levels of tightness according to many measures. However, our view is that labour demand will slow dramatically in 2023 even without a further large drop in GDP growth. The stagflationists also point to the current deflation in goods prices as being only a temporary factor alleviating high inflation, but we think goods price deflation will last for several years.
- Severe recession: Proponents of this scenario point to long lags in the effects of monetary policy, meaning the roughly 5% trough-to-peak increase in the federal-funds rate (the largest tightening cycle in 40 years) will eventually have a crushing effect on the economy. The depletion of excess savings also will weigh on consumption soon.
- Overheating: This camp points to the seemingly unstoppable momentum of the labour market. They also note that other than housing, most of the economy has seemed impervious to the effects of rate hikes. This has been aided by the absence of financial distress.